1 前言
1.1 开发该框架的动机
OpenGL ES 是一个渲染指令接口集合,每渲染一帧图像都是一系列渲染指令的排列组合。常用的渲染指令约有 70 个,记住这些渲染指令及其排列组合方式,是一件痛苦的事情。另外,在图形开发中,经常因为功耗、丢帧等问题需要性能优化,如何从框架层面进行性能优化是一件有挑战的问题。
基于上述原因,笔者手撕了一个 nimi 版的渲染框架,将这些常用的渲染指令有条理地封装、组织、归类,方便愉快并高效地进行 OpenGL ES 渲染开发。笔者在 OpenGL ES 领域从业也有些时日,对现有碎片化的知识进行归纳凝练,形成系统的认知,是件势在必行的事。
1.2 一个 mini 版的渲染框架应该具备哪些能力
一个 mini 版的渲染框架需要对 OpenGL ES 的常用指令进行归类(如下图),封装 EGL、error check、Shader Program、Mesh、VAO、VBO、IBO、Texture、FBO 等类,方便开发者快速开发渲染程序,将更多的注意力聚焦在业务上,而不是如何去组织 OpenGL ES 指令上。
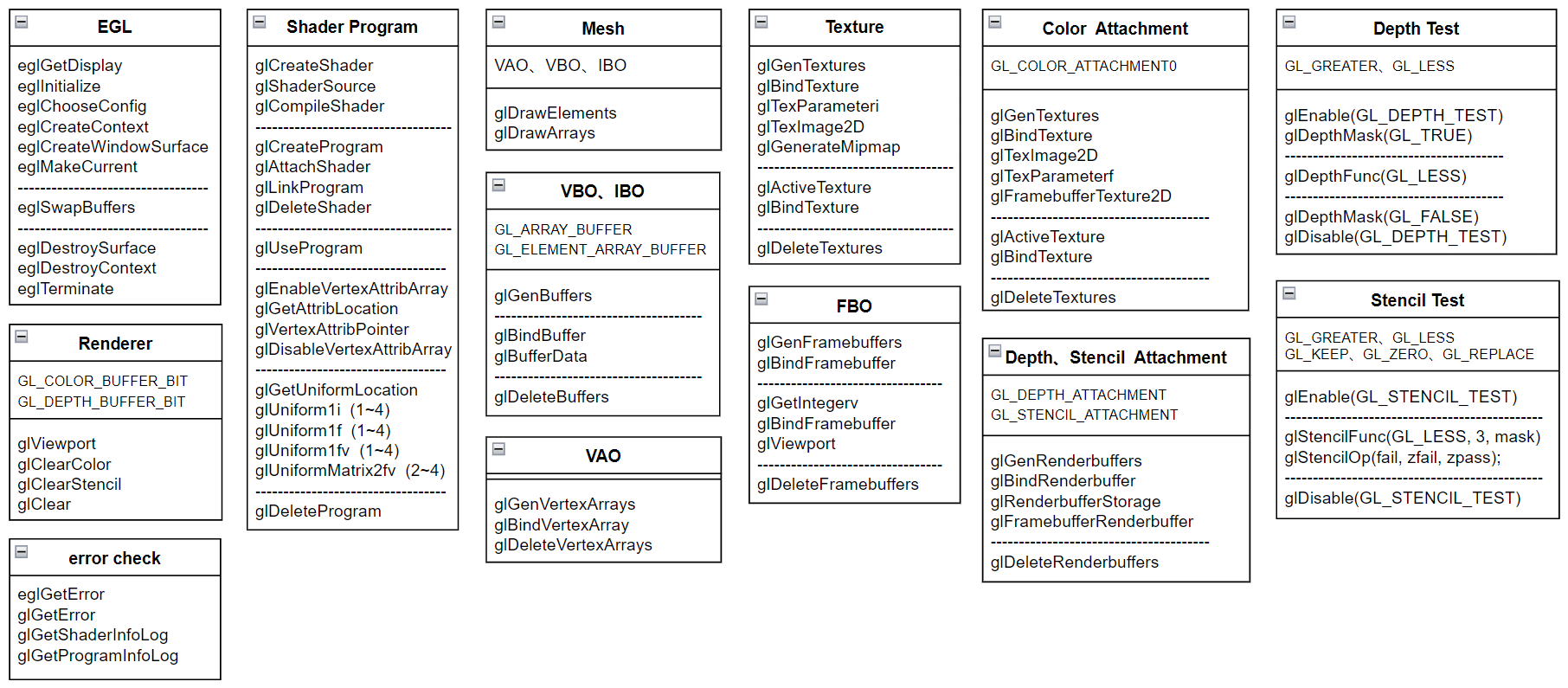
1.3 为什么强调 mini 版渲染框架
从渲染指令的角度来看,OpenGL ES 3.0 约有 300 个渲染指令,本文框架只封装其中最常用的 70 个,指令覆盖程度仍有较大提升空间。
从功能的角度来看,笔者深知一个成熟完备的渲染框架应该具备相机、光源、光照模型(Lambert、Phong、PBR 等)、阴影、射线拾取、重力、碰撞检测、粒子系统等功能。
鉴于上述原因,笔者审慎地保留了 "mini" 前缀。
1.4 本框架的优势
本框架具有以下优势。
- 封装友好:对常用的 EGL 和 GL 指令(约 70 个)进行封装,提供了 EGL 环境搭建、着色器程序生成、网格构建、纹理贴图、离屏渲染、异常检测等基础能力,方便开发者快速开发渲染程序,将精力从繁杂的渲染指令中解放出来,将更多的注意力聚焦到业务上。
- 代码规整:框架中多处设计了 bind 和 unbind 接口,用于绑定和解绑 OpenGL ES 状态机相关 “插槽”,如:VBO、IBO、VAO 中都设计了 bind 和 unbind 接口,ShaderProgram、Texture、FBO、TextureAction 中都设计了 bind 接口;另外,在 FBO 中设计了 begin 和 end 接口,很直观地告诉用户夹在这中间的内容将渲染到 FBO。接口规整简洁,方便用户记忆。
- 易于扩展:定义了 TextureAction 接口,并提供 bind 函数,GLTexture、FBO 都继承了 TextureAction,用户自定义的渲染器或特效类也可以继承 TextureAction,将它们统一视为纹理活动(可绑定),这在特效叠加(或后处理)中非常有用,方便管理多渲染目标图层,易于扩展。
- 性能高效:封装了 VBO、IBO、VAO,用于缓存顶点数据、索引、格式等信息到显存,减少 CPU 到 GPU 的数据传输,提高渲染效率;缓存了 attribute 和 uniform 变量的 location,避免 CPU 频繁向 GPU 查询 location,进一步提高渲染效率;基于 C++ 语言实现渲染框架,代码执行效率较高。
- 跨平台:基于 C++ 语言实现,具有更好的跨平台特性;封装了 core_lib,使得平台相关头文件可以轻松替换;封装了 Application,使得平台相关 api 可以轻松替换。
- 方便调试:设计了 EGL_CALL 和 GL_CALL 两个宏,对每个 EGL 和 GL 指令进行异常检测,方便调试渲染指令,并且通过预编译宏 DEBUG 开关动态控制是否生成异常检测的代码,Release 版本会自动屏蔽异常检测代码,避免带来额外功耗。
2 渲染框架
经过深思熟虑,笔者给该渲染框架命名为 glcore,命名空间也是 glcore。Windows 上 OpenGL 环境搭建主要有 GLFW / freeglut + Glad / GLEW 方案,详见 → Windows上OpenGL环境搭建,本文采用目前广泛使用的 GLFW + Glad 方案。Android 版本的 glcore 实现详见 → 在Android上手撕一个mini版的渲染框架。
本文完整资源(包含 glcore 框架和第 4 节的应用)详见 →【OpenGL ES】一个mini版的Windows渲染框架。
2.1 框架结构
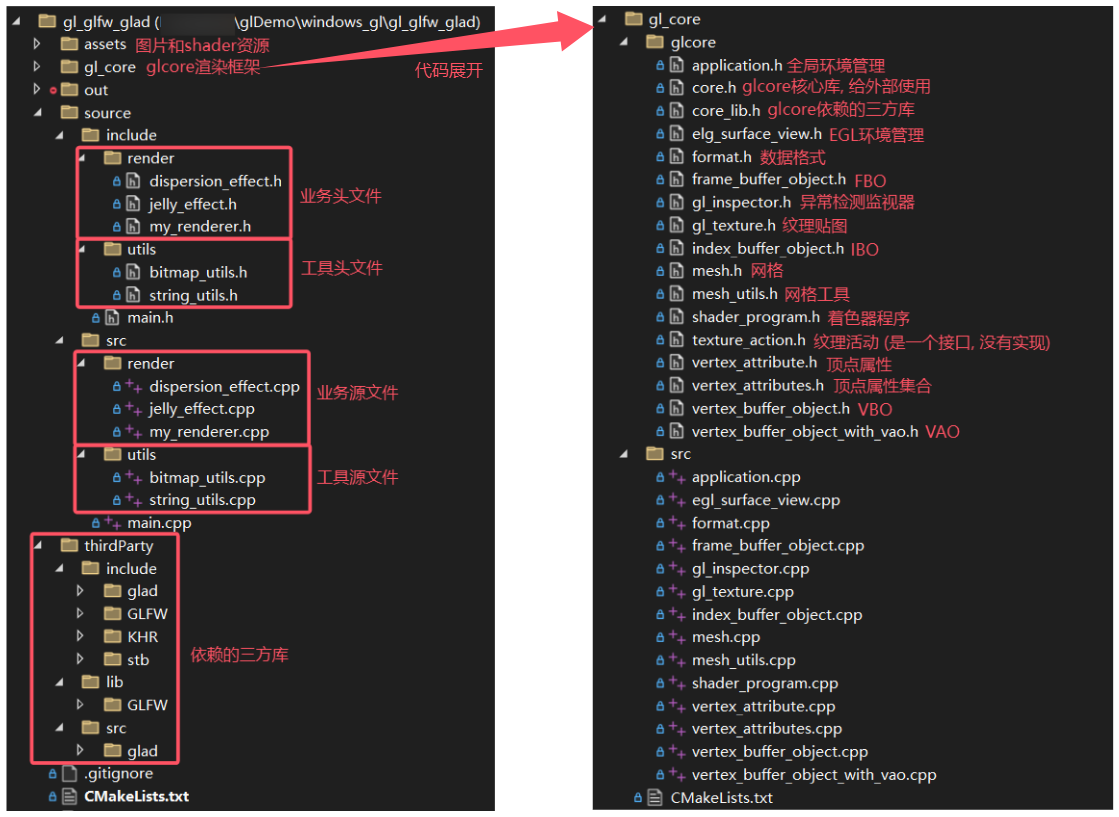
2.2 CMakeLists
CMakeLists.txt
# 设置库名 set(LIB_GL_CORE_NAME "glcore") # 递归添加源文件列表 file(GLOB_RECURSE GL_CORE_SOURCES ./src/ *.cpp) # 添加预构建库 add_library(${LIB_GL_CORE_NAME} ${GL_CORE_SOURCES}) # 将当前目录设为公共头文件目录 (任何链接glcore库的目标都能自动获得这个头文件路径) target_include_directories(${LIB_GL_CORE_NAME} PUBLIC ./) 2.3 核心头文件
核心头文件分为对内和对外的,即内部依赖 core_lib,外部开放 core。
core_lib.h
#pragma once /** * glcore 依赖的核心 GL 库, 便于将 glcore 移植到其他平台 * Android: EGL + GLESv3 * Windows: glfw / freeglut + glad / glew * * @author little fat sheep */ #include <glad/glad.h> #include <GLFW/glfw3.h> 之所以要单独拎出 core_lib.h,是为了方便将该框架迁移到其他平台,如 Android 上依赖的三方渲染库是 EGL + GLESv3,如果不抽出 core_lib.h,就需要将很多地方的 glfw3.h + glad.h 改为 egl.h + gl3.h ,工作量大,也容易漏改。另外,还可以很方便地替换渲染环境,如将 glfw3.h + glad.h 替换为 freeglut.h + glew.h。
core.h
#pragma once /** * glcore核心头文件 * 该头文件是留给外部使用的, glcore内部不能使用, 避免自己包含自己 * @author little fat sheep */ // OpenGL ES API #include "core_lib.h" // glcore 核心头文件 #include "application.h" #include "elg_surface_view.h" #include "format.h" #include "frame_buffer_object.h" #include "gl_inspector.h" #include "gl_texture.h" #include "mesh.h" #include "mesh_utils.h" #include "shader_program.h" #include "texture_action.h" #include "vertex_attribute.h" core.h 只提供给外部使用,方便外部只需要包含一个头文件,就能获取 glcore 的基础能力。
2.4 Application
Application 主要用于管理全局环境,使用单例模式,方便获取一些全局的变量。它也是 glcore 中唯一一个依赖平台相关的接口(除日志 log 接口外),如:m_window 是 Windows 特有的,如果将 glcore 迁移到 Android 中,就需要将该变量替换为 ANativeWindow* 类型,将这些平台相关变量都集中在 Application 中,迁移平台时修改起来也比较容易,避免太分散容易漏掉。另外,还可以很方便地替换渲染环境,如渲染平台替换为 freeglut 时,需要将 GLFWwindow 替换为 void*,因为 freeglut 未提供类似 window 的数据结构。
application.h
#pragma once #include "core_lib.h" #define app Application::getInstance() namespace glcore { /** * 应用程序, 存储全局的参数, 便于访问 * @author little fat sheep */ class Application { private: static Application* sInstance; public: int width = 0; int height = 0; float aspect = 1.0f; private: GLFWwindow* m_window = nullptr; public: static Application* getInstance(); ~Application(); void resize(int width, int height); GLFWwindow* getWindow() { return m_window; } void setWindow(GLFWwindow* window); void releaseWindow(); private: Application() {}; }; } // namespace glcore application.cpp
#include "glcore/application.h" namespace glcore { Application* Application::sInstance = nullptr; Application *Application::getInstance() { if (sInstance == nullptr) { sInstance = new Application(); } return sInstance; } Application::~Application() { } void Application::resize(int width, int height) { this->width = width; this->height = height; this->aspect = (float) width / (float) height; } void Application::setWindow(GLFWwindow* window) { m_window = window; int width, height; glfwGetFramebufferSize(window, &width, &height); resize(width, height); } void Application::releaseWindow() { if (m_window) { m_window = nullptr; } } } // namespace glcore 2.5 GLInspector
GLInspector 主要用于异常信息检测,另外设计了 EGL_CALL 和 GL_CALL 两个宏,分别对 EGL 和 GL 指令进行装饰。如果定义了 DEBUG 宏,就会对每个 EGL 和 GL 指令进行异常检测,方便调试代码;如果未定义了 DEBUG 宏,就不会进行异常检测。
用户可以在 CMakeLists.txt 中添加预编译宏 DEBUG,这样就可以根据 Release 和 Debug 版本自动构建不同的版本。
if (CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE STREQUAL "Debug") # 添加预编译宏 add_definitions(-DDEBUG) endif () gl_inspector.h
#pragma once #include "core_lib.h" #ifdef DEBUG #define EGL_CALL(func) func;GLInspector::checkEGLError(); #define GL_CALL(func) func;GLInspector::checkGLError(); #else #define EGL_CALL(func) func; #define GL_CALL(func) func; #endif namespace glcore { /** * OpenGL ES命令报错监视器 * @author little fat sheep */ class GLInspector { public: static void checkEGLError(const char* tag); // 检查EGL配置 static void checkEGLError(); // 通用检查EGL错误 static void printShaderInfoLog(GLuint shader, const char* tag); // 打印Shader错误日志 static void printProgramInfoLog(GLuint program, const char* tag); // 打印Program错误日志 static void checkGLError(const char* tag); // 检查GL报错信息 static void checkGLError(); // 通用检查GL错误 }; } // namespace glcore gl_inspector.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <assert.h> #include <string> #include "glcore/core_lib.h" #include "glcore/gl_inspector.h" // 以下内容为了不报错临时添加的 (glfw/freeglut已经创建了egl环境) #define EGL_SUCCESS 0x3000 #define EGL_NOT_INITIALIZED 0x3001 #define EGL_BAD_ACCESS 0x3002 #define EGL_BAD_ALLOC 0x3003 #define EGL_BAD_ATTRIBUTE 0x3004 #define EGL_BAD_CONFIG 0x3005 #define EGL_BAD_CONTEXT 0x3006 #define EGL_BAD_SURFACE 0x3007 #define EGL_BAD_DISPLAY 0x3008 #define EGL_BAD_CURRENT_SURFACE 0x3009 #define EGL_BAD_NATIVE_PIXMAP 0x300A #define EGL_BAD_NATIVE_WINDOW 0x300D #define EGL_BAD_PARAMETER 0x300C #define EGL_BAD_MATCH 0x3010 #define EGL_CONTEXT_LOST 0x300E // 以上内容为了不报错临时添加的 #define TAG "GLInspector" int eglGetError() { return 0; } using namespace std; namespace glcore { void GLInspector::checkEGLError(const char *tag) { int error = eglGetError(); if (error != EGL_SUCCESS) { printf("%s: %s failed: 0x%xn", TAG, tag, error); } } void GLInspector::checkEGLError() { GLenum errorCode = eglGetError(); if (errorCode != EGL_SUCCESS) { string error; switch (errorCode) { case EGL_BAD_DISPLAY: error = "EGL_BAD_DISPLAY"; break; case EGL_NOT_INITIALIZED: error = "EGL_NOT_INITIALIZED"; break; case EGL_BAD_CONFIG: error = "EGL_BAD_CONFIG"; break; case EGL_BAD_CONTEXT: error = "EGL_BAD_CONTEXT"; break; case EGL_BAD_NATIVE_WINDOW: error = "EGL_BAD_NATIVE_WINDOW"; break; case EGL_BAD_SURFACE: error = "EGL_BAD_SURFACE"; break; case EGL_BAD_CURRENT_SURFACE: error = "EGL_BAD_CURRENT_SURFACE"; break; case EGL_BAD_ACCESS: error = "EGL_BAD_ACCESS"; break; case EGL_BAD_ALLOC: error = "EGL_BAD_ALLOC"; break; case EGL_BAD_ATTRIBUTE: error = "EGL_BAD_ATTRIBUTE"; break; case EGL_BAD_PARAMETER: error = "EGL_BAD_PARAMETER"; break; case EGL_BAD_NATIVE_PIXMAP: error = "EGL_BAD_NATIVE_PIXMAP"; break; case EGL_BAD_MATCH: error = "EGL_BAD_MATCH"; break; case EGL_CONTEXT_LOST: error = "EGL_CONTEXT_LOST"; break; default: error = "UNKNOW"; break; } printf("checkEGLError failed: %s, 0x%x", error.c_str(), errorCode); assert(false); } } void GLInspector::printShaderInfoLog(GLuint shader, const char* tag) { char infoLog[512]; glGetShaderInfoLog(shader, 512, nullptr, infoLog); printf("%s: %s failed: %sn", TAG, tag, infoLog); } void GLInspector::printProgramInfoLog(GLuint program, const char* tag) { char infoLog[512]; glGetProgramInfoLog(program, 512, nullptr, infoLog); printf("%s: %s failed: %sn", TAG, tag, infoLog); } void GLInspector::checkGLError(const char *tag) { GLenum error = glGetError(); if(error != GL_NO_ERROR) { printf("%s: %s failed: 0x%xn", TAG, tag, error); } } void GLInspector::checkGLError() { GLenum errorCode = glGetError(); if (errorCode != GL_NO_ERROR) { string error; switch (errorCode) { case GL_INVALID_ENUM: error = "GL_INVALID_ENUM"; break; case GL_INVALID_VALUE: error = "GL_INVALID_VALUE"; break; case GL_INVALID_OPERATION: error = "GL_INVALID_OPERATION"; break; case GL_INVALID_INDEX: error = "GL_INVALID_INDEX"; break; case GL_INVALID_FRAMEBUFFER_OPERATION: error = "GL_INVALID_FRAMEBUFFER_OPERATION"; break; case GL_OUT_OF_MEMORY: error = "GL_OUT_OF_MEMORY"; break; default: error = "UNKNOW"; break; } printf("checkError failed: %s, 0x%xn", error.c_str(), errorCode); assert(false); } } } // namespace glcore 2.6 EGLSurfaceView
EGLSurfaceView 主要承载了 EGL 环境搭建。EGL 详细介绍见 → 【OpenGL ES】EGL+FBO离屏渲染。
由于 GLFW 中已经创建了 EGL 环境,EGLSurfaceView 实际上是多余的,为了保持 glcore 在各个平台上的代码具有高度一致性,并且方便随时自主创建 EGL 环境,这里仍然保留了 EGLSurfaceView。本文中主要使用到 EGLSurfaceView 的内部类 Renderer,起到定制渲染流程规范的作用。
elg_surface_view.h
#pragma once #include "core_lib.h" // 以下内容为了不报错临时添加的 (glfw/freeglut创建了egl环境) typedef void* EGLDisplay; typedef void* EGLConfig; typedef void* EGLContext; typedef void* EGLSurface; // 以上内容为了不报错临时添加的 namespace glcore { /** * EGL环境封装类 * glfw和freeglut中创建了egl环境, 因此该类可以去掉, * 但是为了方便将glcore迁移到需要用户搭建egl环境的平台中, * 暂时保留该类. * * @author little fat sheep */ class EGLSurfaceView { public: class Renderer; private: Renderer* m_renderer = nullptr; EGLDisplay m_eglDisplay; EGLConfig m_eglConfig; EGLContext m_eglContext; EGLSurface m_eglSurface; bool m_firstCreateSurface = true; public: EGLSurfaceView(); ~EGLSurfaceView(); void setRenderer(Renderer* renderer); bool surfaceCreated(); void surfaceChanged(int width, int height); void drawFrame(); void surfaceDestroy(); private: void createDisplay(); void createConfig(); void createContext(); void createSurface(); void makeCurrent(); public: /** * 渲染器接口, 类比GLSurfaceView.Renderer * @author little fat sheep */ class Renderer { public: virtual ~Renderer() {}; virtual void onSurfaceCreated() = 0; virtual void onSurfaceChanged(int width, int height) = 0; virtual void onDrawFrame() = 0; }; }; } // namespace glcore elg_surface_view.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "glcore/application.h" #include "glcore/elg_surface_view.h" #include "glcore/gl_inspector.h" #define TAG "EGLSurfaceView" // 以下内容为了不报错临时添加的 (glfw/freeglut已经创建了egl环境) #define EGL_RED_SIZE 0x3024 #define EGL_GREEN_SIZE 0x3023 #define EGL_BLUE_SIZE 0x3022 #define EGL_ALPHA_SIZE 0x3021 #define EGL_DEPTH_SIZE 0x3025 #define EGL_RENDERABLE_TYPE 0x3040 #define EGL_OPENGL_ES3_BIT 0x0040 #define EGL_SURFACE_TYPE 0x3033 #define EGL_WINDOW_BIT 0x0004 #define EGL_NONE 0x3038 #define EGL_CONTEXT_CLIENT_VERSION 0x3098 #define EGL_DEFAULT_DISPLAY ((EGLDisplay)0) #define EGL_NO_DISPLAY ((EGLDisplay)0) #define EGL_NO_CONTEXT ((EGLContext)0) #define EGL_NO_SURFACE ((EGLSurface)0) typedef int32_t EGLint; EGLDisplay eglGetDisplay(EGLDisplay a1) { return nullptr; } void eglInitialize(EGLDisplay a1, int* a3, int* a4) {} void eglChooseConfig(EGLDisplay a1, const EGLint* a2, EGLConfig* a3, EGLint a4, EGLint* a5) {} EGLContext eglCreateContext(EGLDisplay a1, EGLConfig a2, EGLContext a3, const EGLint* a4) { return nullptr; } EGLSurface eglCreateWindowSurface(EGLDisplay a1, EGLConfig a2, void* a3, const EGLint* a4) { return nullptr; } void eglMakeCurrent(EGLDisplay a1, EGLSurface a2, EGLSurface a3, EGLContext a4) {} void eglSwapBuffers(EGLDisplay a1, EGLSurface a2) {} void eglDestroySurface(EGLDisplay a1, EGLSurface a2) {} void eglDestroyContext(EGLDisplay a1, EGLContext a2) {} void eglTerminate(EGLDisplay a1) {} // 以上内容为了不报错临时添加的 namespace glcore { EGLSurfaceView::EGLSurfaceView() { printf("%s: initn", TAG); createDisplay(); createConfig(); createContext(); } EGLSurfaceView::~EGLSurfaceView() { printf("%s: destroyn", TAG); if (m_renderer) { delete m_renderer; m_renderer = nullptr; } if (m_eglDisplay && m_eglDisplay != EGL_NO_DISPLAY) { // 与显示设备解绑 EGL_CALL(eglMakeCurrent(m_eglDisplay, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT)); // 销毁 EGLSurface if (m_eglSurface && m_eglSurface != EGL_NO_SURFACE) { EGL_CALL(eglDestroySurface(m_eglDisplay, m_eglSurface)); delete &m_eglSurface; } // 销毁 EGLContext if (m_eglContext && m_eglContext != EGL_NO_CONTEXT) { EGL_CALL(eglDestroyContext(m_eglDisplay, m_eglContext)); delete &m_eglContext; } // 销毁 EGLDisplay (显示设备) EGL_CALL(eglTerminate(m_eglDisplay)); delete &m_eglDisplay; } app->releaseWindow(); delete app; } void EGLSurfaceView::setRenderer(Renderer *renderer) { printf("%s: setRenderern", TAG); m_renderer = renderer; } bool EGLSurfaceView::surfaceCreated() { printf("%s: surfaceCreatedn", TAG); app->resize(app->width, app->height); createSurface(); makeCurrent(); if (m_renderer && m_firstCreateSurface) { m_renderer->onSurfaceCreated(); m_firstCreateSurface = false; } return true; } void EGLSurfaceView::surfaceChanged(int width, int height) { printf("%s: surfaceChanged, width: %d, height: %dn", TAG, width, height); app->resize(width, height); if (m_renderer) { m_renderer->onSurfaceChanged(width, height); } } void EGLSurfaceView::drawFrame() { if (!m_eglSurface || m_eglSurface == EGL_NO_SURFACE || !m_renderer) { return; } m_renderer->onDrawFrame(); EGL_CALL(eglSwapBuffers(m_eglDisplay, m_eglSurface)); } void EGLSurfaceView::surfaceDestroy() { printf("%s: surfaceDestroyn", TAG); if (m_eglDisplay && m_eglDisplay != EGL_NO_DISPLAY) { // 与显示设备解绑 EGL_CALL(eglMakeCurrent(m_eglDisplay, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT)); // 销毁 EGLSurface if (m_eglSurface && m_eglSurface != EGL_NO_SURFACE) { EGL_CALL(eglDestroySurface(m_eglDisplay, m_eglSurface)); m_eglSurface = nullptr; } } app->releaseWindow(); } // 1.创建EGLDisplay void EGLSurfaceView::createDisplay() { EGL_CALL(m_eglDisplay = eglGetDisplay(EGL_DEFAULT_DISPLAY)); EGL_CALL(eglInitialize(m_eglDisplay, nullptr, nullptr)); } // 2.创建EGLConfig void EGLSurfaceView::createConfig() { if (m_eglDisplay && m_eglDisplay != EGL_NO_DISPLAY) { const EGLint configAttrs[] = { EGL_RED_SIZE, 8, EGL_GREEN_SIZE, 8, EGL_BLUE_SIZE, 8, EGL_ALPHA_SIZE, 8, EGL_DEPTH_SIZE, 8, EGL_RENDERABLE_TYPE, EGL_OPENGL_ES3_BIT, EGL_SURFACE_TYPE, EGL_WINDOW_BIT, EGL_NONE }; EGLint numConfigs; EGL_CALL(eglChooseConfig(m_eglDisplay, configAttrs, &m_eglConfig, 1, &numConfigs)); } } // 3.创建EGLContext void EGLSurfaceView::createContext() { if (m_eglConfig) { const EGLint contextAttrs[] = { EGL_CONTEXT_CLIENT_VERSION, 3, EGL_NONE }; EGL_CALL(m_eglContext = eglCreateContext(m_eglDisplay, m_eglConfig, EGL_NO_CONTEXT, contextAttrs)); } } // 4.创建EGLSurface void EGLSurfaceView::createSurface() { if (m_eglContext && m_eglContext != EGL_NO_CONTEXT) { EGL_CALL(m_eglSurface = eglCreateWindowSurface(m_eglDisplay, m_eglConfig, app->getWindow(), nullptr)); } } // 5.绑定EGLSurface和EGLContext到显示设备(EGLDisplay) void EGLSurfaceView::makeCurrent() { if (m_eglSurface && m_eglSurface != EGL_NO_SURFACE) { EGL_CALL(eglMakeCurrent(m_eglDisplay, m_eglSurface, m_eglSurface, m_eglContext)); } } } // namespace glcore 2.7 ShaderProgram
ShaderProgram 主要用于编译 Shader、链接 Program、设置 attribute 属性、更新 uniform 属性。
glGetAttribLocation、glGetUniformLocation 两个接口需要 CPU 向 GPU 查询 location 信息,并且会频繁调用,为提高性能,笔者设计了 m_attributes 和 m_uniforms 两个 map 存储 name 到 location 的映射,方便快速获取 location,避免 CPU 频繁与 GPU 交互,以提高渲染性能。
shader_program.h
#pragma once #include <map> #include "core_lib.h" using namespace std; namespace glcore { /** * 着色器程序 * @author little fat sheep */ class ShaderProgram { public: static constexpr char* ATTRIBUTE_POSITION = "a_position"; // 着色器中位置属性名 static constexpr char* ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL = "a_normal"; // 着色器中位法线性名 static constexpr char* ATTRIBUTE_COLOR = "a_color"; // 着色器中颜色属性名 static constexpr char* ATTRIBUTE_TEXCOORD = "a_texCoord"; // 着色器中纹理坐标属性名 static constexpr char* ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT = "a_tangent"; // 着色器中切线属性名 static constexpr char* ATTRIBUTE_BINORMAL = "a_binormal"; // 着色器中副切线属性名 static constexpr char* UNIFORM_TEXTURE = "u_texture"; // 着色器中纹理名 static constexpr char* UNIFORM_VP = "u_projectionViewMatrix"; // 着色器中VP名 private: GLuint m_program; map<const char*, int> m_attributes; map<const char*, int> m_uniforms; public: ShaderProgram(const char* vertexCode, const char* fragmentCode); ~ShaderProgram(); void bind(); GLuint getHandle() { return m_program; } // 操作attribute属性 void enableVertexAttribArray(const char* name); void enableVertexAttribArray(int location); void setVertexAttribPointer(const char* name, int size, int type, bool normalize, int stride, int offset); void setVertexAttribPointer(int location, int size, int type, bool normalize, int stride, int offset); void disableVertexAttribArray(const char* name); void disableVertexAttribArray(int location); // 操作uniform属性 void setUniformi(const char* name, int value); void setUniformi(int location, int value); void setUniformi(const char* name, int value1, int value2); void setUniformi(int location, int value1, int value2); void setUniformi(const char* name, int value1, int value2, int value3); void setUniformi(int location, int value1, int value2, int value3); void setUniformi(const char* name, int value1, int value2, int value3, int value4); void setUniformi(int location, int value1, int value2, int value3, int value4); void setUniformf(const char* name, float value); void setUniformf(int location, float value); void setUniformf(const char* name, float value1, float value2); void setUniformf(int location, float value1, float value2); void setUniformf(const char* name, float value1, float value2, int value3); void setUniformf(int location, float value1, float value2, int value3); void setUniformf(const char* name, float value1, float value2, int value3, int value4); void setUniformf(int location, float value1, float value2, int value3, int value4); void setUniform1fv(const char* name, int length, const float values[]); void setUniform1fv(int location, int count, float const values[]); void setUniform2fv(const char* name, int count, const float values[]); void setUniform2fv(int location, int count, const float values[]); void setUniform3fv(const char* name, int count, const float values[]); void setUniform3fv(int location, int count, const float values[]); void setUniform4fv(const char* name, int count, const float values[]); void setUniform4fv(int location, int count, const float values[]); void setUniformMatrix2fv(const char* name, int count, bool transpose, const float *value); void setUniformMatrix2fv(int location, int count, bool transpose, const float *value); void setUniformMatrix3fv(const char* name, int count, bool transpose, const float *value); void setUniformMatrix3fv(int location, int count, bool transpose, const float *value); void setUniformMatrix4fv(const char* name, int count, bool transpose, const float *value); void setUniformMatrix4fv(int location, int count, bool transpose, const float *value); int fetchAttributeLocation(const char* name); int fetchUniformLocation(const char* name); private: void compileShaders(const char* vertexCode, const char* fragmentCode); GLuint loadShader(GLenum type, const char* source); GLuint linkProgram(GLuint vertexShader, GLuint fragmentShader); }; } // namespace glcore shader_program.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "glcore/gl_inspector.h" #include "glcore/shader_program.h" #define TAG "ShaderProgram" namespace glcore { ShaderProgram::ShaderProgram(const char* vertexCode, const char* fragmentCode) { compileShaders(vertexCode, fragmentCode); } ShaderProgram::~ShaderProgram() { if (m_program) { GL_CALL(glUseProgram(0)); GL_CALL(glDeleteProgram(m_program)); m_program = 0; } m_attributes.clear(); m_uniforms.clear(); } void ShaderProgram::bind() { GL_CALL(glUseProgram(m_program)); } void ShaderProgram::enableVertexAttribArray(const char* name) { int location = fetchAttributeLocation(name); enableVertexAttribArray(location); } void ShaderProgram::enableVertexAttribArray(int location) { GL_CALL(glEnableVertexAttribArray(location)); } void ShaderProgram::setVertexAttribPointer(const char *name, int size, int type, bool normalize, int stride, int offset) { int location = fetchAttributeLocation(name); setVertexAttribPointer(location, size, type, normalize, stride, offset); } void ShaderProgram::setVertexAttribPointer(int location, int size, int type, bool normalize, int stride, int offset) { GL_CALL(glVertexAttribPointer(location, size, type, normalize, stride, (void*) offset)); } void ShaderProgram::disableVertexAttribArray(const char* name) { int location = fetchAttributeLocation(name); disableVertexAttribArray(location); } void ShaderProgram::disableVertexAttribArray(int location) { GL_CALL(glDisableVertexAttribArray(location)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformi(const char* name, int value) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniform1i(location, value)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformi(int location, int value) { GL_CALL(glUniform1i(location, value)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformi(const char* name, int value1, int value2) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniform2i(location, value1, value2)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformi(int location, int value1, int value2) { GL_CALL(glUniform2i(location, value1, value2)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformi(const char* name, int value1, int value2, int value3) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniform3i(location, value1, value2, value3)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformi(int location, int value1, int value2, int value3) { GL_CALL(glUniform3i(location, value1, value2, value3)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformi(const char* name, int value1, int value2, int value3, int value4) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniform4i(location, value1, value2, value3, value4)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformi(int location, int value1, int value2, int value3, int value4) { GL_CALL(glUniform4i(location, value1, value2, value3, value4)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformf(const char* name, float value) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniform1f(location, value)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformf(int location, float value) { GL_CALL(glUniform1f(location, value)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformf(const char* name, float value1, float value2) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniform2f(location, value1, value2)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformf(int location, float value1, float value2) { GL_CALL(glUniform2f(location, value1, value2)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformf(const char* name, float value1, float value2, int value3) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniform3f(location, value1, value2, value3)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformf(int location, float value1, float value2, int value3) { GL_CALL(glUniform3f(location, value1, value2, value3)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformf(const char* name, float value1, float value2, int value3, int value4) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniform4f(location, value1, value2, value3, value4)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformf(int location, float value1, float value2, int value3, int value4) { GL_CALL(glUniform4f(location, value1, value2, value3, value4)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniform1fv(const char* name, int count, const float values[]) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniform1fv(location, count, values)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniform1fv(int location, int count, const float values[]) { GL_CALL(glUniform1fv(location, count, values)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniform2fv(const char* name, int count, const float values[]) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniform2fv(location, count / 2, values)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniform2fv(int location, int count, const float values[]) { GL_CALL(glUniform2fv(location, count / 2, values)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniform3fv(const char* name, int count, const float values[]) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniform3fv(location, count / 3, values)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniform3fv(int location, int count, const float values[]) { GL_CALL(glUniform3fv(location, count / 3, values)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniform4fv(const char* name, int count, const float values[]) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniform4fv(location, count / 4, values)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniform4fv(int location, int count, const float values[]) { GL_CALL(glUniform4fv(location, count / 4, values)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformMatrix2fv(const char* name, int count, bool transpose, const float *value) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniformMatrix2fv(location, count, transpose, value)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformMatrix2fv(int location, int count, bool transpose, const float *value) { GL_CALL(glUniformMatrix2fv(location, count, transpose, value)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformMatrix3fv(const char* name, int count, bool transpose, const float *value) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniformMatrix3fv(location, count, transpose, value)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformMatrix3fv(int location, int count, bool transpose, const float *value) { GL_CALL(glUniformMatrix3fv(location, count, transpose, value)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformMatrix4fv(const char* name, int count, bool transpose, const float *value) { int location = fetchUniformLocation(name); GL_CALL(glUniformMatrix4fv(location, count, transpose, value)); } void ShaderProgram::setUniformMatrix4fv(int location, int count, bool transpose, const float *value) { GL_CALL(glUniformMatrix4fv(location, count, transpose, value)); } int ShaderProgram::fetchAttributeLocation(const char* name) { int location; auto it = m_attributes.find(name); if (it == m_attributes.end()) { GL_CALL(location = glGetAttribLocation(m_program, name)); if (location == -1) { printf("%s: no attribute: %sn", TAG, name); //GLInspector::printProgramInfoLog(m_program, "fetchAttributeLocation"); return -1; } m_attributes[name] = location; } else { location = it->second; } return location; } int ShaderProgram::fetchUniformLocation(const char* name) { int location; auto it = m_uniforms.find(name); if (it == m_uniforms.end()) { GL_CALL(location = glGetUniformLocation(m_program, name)); if (location == -1) { printf("%s: no uniform: %sn", TAG, name); //GLInspector::printProgramInfoLog(m_program, "fetchUniformLocation"); return -1; } m_uniforms[name] = location; } else { location = it->second; } return location; } void ShaderProgram::compileShaders(const char* vertexCode, const char* fragmentCode) { GLuint vertexShader = loadShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER, vertexCode); GLuint fragmentShader = loadShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, fragmentCode); m_program = linkProgram(vertexShader, fragmentShader); } GLuint ShaderProgram::loadShader(GLenum type, const char* source) { GL_CALL(GLuint shader = glCreateShader(type)); GL_CALL(glShaderSource(shader, 1, &source, nullptr)); GL_CALL(glCompileShader(shader)); GLint success; glGetShaderiv(shader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &success); if (!success) { GLInspector::printShaderInfoLog(shader, "loadShader"); return 0; } return shader; } GLuint ShaderProgram::linkProgram(GLuint vertexShader, GLuint fragmentShader) { GL_CALL(GLuint program = glCreateProgram()); GL_CALL(glAttachShader(program, vertexShader)); GL_CALL(glAttachShader(program, fragmentShader)); GL_CALL(glLinkProgram(program)); GLint success; glGetProgramiv(program, GL_LINK_STATUS, &success); if (!success) { GLInspector::printProgramInfoLog(m_program, "linkProgram"); } GL_CALL(glDeleteShader(vertexShader)); GL_CALL(glDeleteShader(fragmentShader)); return program; } } // namespace glcore 2.8 VBO
VBO 是 Vertex Buffer Object 的简称,即顶点缓冲对象,作用是缓存顶点数据到显存中,避免频繁调用 glVertexAttribPointer 传输顶点数据,减少 CPU 到 GPU 的数据传输,提高渲染效率。
顶点属性主要有位置、颜色、纹理坐标、法线、切线、副切线等,每个属性又有属性标识、维数、是否已标准化、数据类型、偏移、别名、纹理单元等。
由于 VBO 中有多个属性数据,每个属性有多个字段,笔者除了封装 VertexBufferObject 类,还封装了 VertexAttributes 和 VertexAttribute 两个类。VertexAttribute 是属性描述类,VertexAttributes 是属性描述集合。
vertex_buffer_object.h
#pragma once #include <initializer_list> #include <vector> #include "core_lib.h" #include "shader_program.h" #include "vertex_attributes.h" #include "vertex_attribute.h" #include "vertex_attributes.h" using namespace std; namespace glcore { /** * 顶点属性缓冲对象 (简称VBO) * @author little fat sheep */ class VertexBufferObject { protected: bool m_isBound = false; // 是否已绑定到VBO (或VAO) bool m_isDirty = false; // 是否有脏数据 (缓存的数据需要更新) private: GLuint m_vboHandle; // VBO句柄 VertexAttributes* m_attributes; // 顶点属性 GLuint m_usage; // GL_STATIC_DRAW 或 GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW const float* m_vertices; // 顶点属性数据 int m_vertexNum = 0; // 顶点个数 int m_bytes = 0; // 顶点属性字节数 public: VertexBufferObject(bool isStatic, initializer_list<VertexAttribute*> attributes); VertexBufferObject(bool isStatic, VertexAttributes* attributes); virtual ~VertexBufferObject(); void setVertices(float* vertices, int bytes); void bind(ShaderProgram* shader); virtual void bind(ShaderProgram* shader, int* locations); void unbind(ShaderProgram* shader); virtual void unbind(ShaderProgram* shader, int* locations); int getNumVertices() { return m_vertexNum; } private: void applyBufferData(); // 缓存数据 }; } // namespace glcore vertex_buffer_object.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "glcore/gl_inspector.h" #include "glcore/vertex_buffer_object.h" #define TAG "VertexBufferObject" namespace glcore { VertexBufferObject::VertexBufferObject(bool isStatic, initializer_list<VertexAttribute*> attributes): VertexBufferObject(isStatic, new VertexAttributes(attributes)) { } VertexBufferObject::VertexBufferObject(bool isStatic, VertexAttributes* attributes): m_attributes(attributes) { m_usage = isStatic ? GL_STATIC_DRAW : GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW; GL_CALL(glGenBuffers(1, &m_vboHandle)); printf("%s: init: %dn", TAG, m_vboHandle); } VertexBufferObject::~VertexBufferObject() { printf("%s: destroyn", TAG); GL_CALL(glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0)); GL_CALL(glDeleteBuffers(1, &m_vboHandle)); m_vboHandle = 0; delete m_attributes; delete[] m_vertices; } void VertexBufferObject::setVertices(float* vertices, int bytes) { m_vertices = vertices; m_vertexNum = bytes / m_attributes->vertexSize; m_bytes = bytes; m_isDirty = true; if (m_isBound) { applyBufferData(); } } void VertexBufferObject::bind(ShaderProgram* shader) { bind(shader, nullptr); } void VertexBufferObject::bind(ShaderProgram* shader, int* locations) { GL_CALL(glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, m_vboHandle)); if (m_isDirty) { applyBufferData(); } if (locations == nullptr) { for (int i = 0; i < m_attributes->size(); i++) { VertexAttribute* attribute = m_attributes->get(i); shader->enableVertexAttribArray(attribute->alias); shader->setVertexAttribPointer(attribute->alias, attribute->numComponents, attribute->type, attribute->normalized, m_attributes->vertexSize, attribute->offset); } } else { for (int i = 0; i < m_attributes->size(); i++) { VertexAttribute* attribute = m_attributes->get(i); shader->enableVertexAttribArray(locations[i]); shader->setVertexAttribPointer(locations[i], attribute->numComponents, attribute->type, attribute->normalized, m_attributes->vertexSize, attribute->offset); } } m_isBound = true; } void VertexBufferObject::unbind(ShaderProgram* shader) { unbind(shader, nullptr); } void VertexBufferObject::unbind(ShaderProgram* shader, int* locations) { if (locations == nullptr) { for (int i = 0; i < m_attributes->size(); i++) { shader->disableVertexAttribArray(m_attributes->get(i)->alias); } } else { for (int i = 0; i < m_attributes->size(); i++) { shader->disableVertexAttribArray(locations[i]); } } m_isBound = false; } void VertexBufferObject::applyBufferData() { GL_CALL(glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, m_bytes, m_vertices, m_usage)); m_isDirty = false; } } // namespace glcore vertex_attributes.h
#pragma once #include <initializer_list> #include <vector> #include "vertex_attribute.h" using namespace std; namespace glcore { /** * 顶点属性集(位置、颜色、纹理坐标、法线、切线、副切线等中的一部分) * 每个顶点属性可以看作一个通道, 这个通道可能是多维的, 每个维度可能是多字节的 * @author little fat sheep */ class VertexAttributes { public: int vertexSize; // 所有顶点属性的字节数 private: vector<VertexAttribute*> m_attributes; // 顶点属性列表 public: VertexAttributes(initializer_list<VertexAttribute*> attributes); ~VertexAttributes(); VertexAttribute* get(int index); // 根据索引获取属性 int size(); // 获取属性个数 private: int calculateOffsets(); // 计算偏移 }; /** * 顶点属性标识 * @author little fat sheep */ class Usage { public: static const int Position = 1; static const int ColorUnpacked = 2; static const int ColorPacked = 4; static const int Normal = 8; static const int TextureCoordinates = 16; static const int Tangent = 32; static const int BiNormal = 64; }; } // namespace glcore vertex_attributes.cpp
#include "glcore/vertex_attributes.h" namespace glcore { VertexAttributes::VertexAttributes(initializer_list<VertexAttribute*> attributes): m_attributes(attributes) { vertexSize = calculateOffsets(); } VertexAttributes::~VertexAttributes() { m_attributes.clear(); } VertexAttribute* VertexAttributes::get(int index) { if (index >= 0 && index < m_attributes.size()) { return m_attributes[index]; } return nullptr; } int VertexAttributes::size() { return m_attributes.size(); } int VertexAttributes::calculateOffsets() { int count = 0; for (VertexAttribute* attribute : m_attributes) { attribute->offset = count; count += attribute->getSizeInBytes(); } return count; } } // namespace glcore vertex_attribute.h
#pragma once namespace glcore { /** * 单个顶点属性(位置、颜色、纹理坐标、法线、切线、副切线等中的一个) * 每个顶点属性可以看作一个通道, 这个通道可能是多维的, 每个维度可能是多字节的 * @author little fat sheep */ class VertexAttribute { public: int usage; // 顶点属性标识 int numComponents; // 顶点属性维数 (如顶点坐标属性是3维的, 纹理坐标是2维的) bool normalized; // 顶点属性是否已经标准化 (有符号: -1~1, 无符号: 0~1) int type; // 顶点属性的变量类型 (GL_FLOAT、GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE等) int offset; // 顶点属性在字节上的偏移 const char* alias; // 顶点属性别名 (着色器中变量名) int unit; // 纹理单元 (可能有多个纹理, 可选) public: VertexAttribute(int usage, int numComponents, const char* alias); VertexAttribute(int usage, int numComponents, const char* alias, int unit); VertexAttribute(int usage, int numComponents, int type, bool normalized, const char* alias); VertexAttribute(int usage, int numComponents, int type, bool normalized, const char* alias, int unit); ~VertexAttribute(); static VertexAttribute* Position(); // 位置参数信息 static VertexAttribute* TexCoords(int unit); // 纹理坐标参数信息 static VertexAttribute* Normal(); // 法线参数信息 static VertexAttribute* ColorPacked(); // 颜色参数信息 static VertexAttribute* ColorUnpacked(); // 颜色参数信息 static VertexAttribute* Tangent(); // 切线参数信息 static VertexAttribute* Binormal(); // 副切线参数信息 int getSizeInBytes(); // 属性对应的字节数 private: void create(int usage, int numComponents, int type, bool normalized, const char* alias, int unit); }; } // namespace glcore vertex_attribute.cpp
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include "glcore/core_lib.h" #include "glcore/shader_program.h" #include "glcore/vertex_attribute.h" #include "glcore/vertex_attributes.h" #define TAG "VertexAttribute" using namespace std; namespace glcore { VertexAttribute::VertexAttribute(int usage, int numComponents, const char* alias): VertexAttribute(usage, numComponents, alias, 0) { } VertexAttribute::VertexAttribute(int usage, int numComponents, const char* alias, int unit) { int type = usage == Usage::ColorPacked ? GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE : GL_FLOAT; bool normalized = usage == Usage::ColorPacked; create(usage, numComponents, type, normalized, alias, unit); } VertexAttribute::VertexAttribute(int usage, int numComponents, int type, bool normalized, const char* alias) { create(usage, numComponents, type, normalized, alias, 0); } VertexAttribute::VertexAttribute(int usage, int numComponents, int type, bool normalized, const char* alias, int unit) { create(usage, numComponents, type, normalized, alias, unit); } VertexAttribute::~VertexAttribute() { free((void*)alias); } VertexAttribute* VertexAttribute::Position() { return new VertexAttribute(Usage::Position, 3, ShaderProgram::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION); } VertexAttribute* VertexAttribute::TexCoords(int unit) { string str = string(ShaderProgram::ATTRIBUTE_TEXCOORD) + to_string(unit); // 复制字符串, 避免str被回收导致悬垂指针问题, 通过free((void*)alias)释放内存 const char* combined = strdup(str.c_str()); return new VertexAttribute(Usage::TextureCoordinates, 2, combined, unit); } VertexAttribute* VertexAttribute::Normal() { return new VertexAttribute(Usage::Normal, 3, ShaderProgram::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL); } VertexAttribute* VertexAttribute::ColorPacked() { return new VertexAttribute(Usage::ColorPacked, 4, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, true, ShaderProgram::ATTRIBUTE_COLOR); } VertexAttribute* VertexAttribute::ColorUnpacked() { return new VertexAttribute(Usage::ColorUnpacked, 4, GL_FLOAT, false, ShaderProgram::ATTRIBUTE_COLOR); } VertexAttribute* VertexAttribute::Tangent() { return new VertexAttribute(Usage::Tangent, 3, ShaderProgram::ATTRIBUTE_TANGENT); } VertexAttribute* VertexAttribute::Binormal() { return new VertexAttribute(Usage::BiNormal, 3, ShaderProgram::ATTRIBUTE_BINORMAL); } int VertexAttribute::getSizeInBytes() { switch (type) { case GL_FLOAT: case GL_FIXED: return 4 * numComponents; case GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE: case GL_BYTE: return numComponents; case GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT: case GL_SHORT: return 2 * numComponents; } return 0; } void VertexAttribute::create(int usage, int numComponents, int type, bool normalized, const char* alias, int unit) { this->usage = usage; this->numComponents = numComponents; this->type = type; this->normalized = normalized; this->alias = alias; this->unit = unit; printf("%s: create, alias: %sn", TAG, alias); } } // namespace glcore 2.9 VAO
VAO 是 Vertex Array Object 的简称,即顶点数组对象,作用是缓存顶点属性的指针和描述(或格式)信息,简化顶点属性设置的流程,避免频繁调用 glVertexAttribPointer 设置属性描述(或格式)信息,减少 CPU 与 GPU 的交互,提高渲染效率。
vertex_buffer_object_with_vao.h
#pragma once #include <initializer_list> #include "core_lib.h" #include "vertex_buffer_object.h" namespace glcore { /** * 携带VAO的顶点属性缓冲对象 * @author little fat sheep */ class VertexBufferObjectWithVAO : public VertexBufferObject { private: GLuint m_vaoHandle; // VAO句柄 public: VertexBufferObjectWithVAO(bool isStatic, initializer_list<VertexAttribute*> attributes); VertexBufferObjectWithVAO(bool isStatic, VertexAttributes* attributes); ~VertexBufferObjectWithVAO() override; void bind(ShaderProgram* shader, int* locations) override; void unbind(ShaderProgram* shader, int* locations) override; }; } // namespace glcore vertex_buffer_object_with_vao.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "glcore/gl_inspector.h" #include "glcore/vertex_buffer_object_with_vao.h" #define TAG "VertexBufferObjectWithVAO" namespace glcore { VertexBufferObjectWithVAO::VertexBufferObjectWithVAO(bool isStatic, initializer_list<VertexAttribute*> attributes): VertexBufferObjectWithVAO(isStatic, new VertexAttributes(attributes)) { } VertexBufferObjectWithVAO::VertexBufferObjectWithVAO(bool isStatic, VertexAttributes* attributes): VertexBufferObject(isStatic, attributes) { GL_CALL(glGenVertexArrays(1, &m_vaoHandle)); printf("%s: init: %dn", TAG, m_vaoHandle); } VertexBufferObjectWithVAO::~VertexBufferObjectWithVAO() { printf("%s: destroyn", TAG); GL_CALL(glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &m_vaoHandle)); } void VertexBufferObjectWithVAO::bind(ShaderProgram* shader, int* locations) { GL_CALL(glBindVertexArray(m_vaoHandle)); if (m_isDirty) { VertexBufferObject::bind(shader, locations); } m_isBound = true; } void VertexBufferObjectWithVAO::unbind(ShaderProgram* shader, int* locations) { GL_CALL(glBindVertexArray(0)); m_isBound = false; } } // namespace glcore 2.10 IBO
IBO 是 Index Buffer Object 的简称,即索引缓冲对象,作用是缓存顶点索引到显存中,避免频繁调用 glDrawElements 传输顶点索引,减少 CPU 到 GPU 的数据传输,提高渲染效率。由于 IBO 绑定的是 OpenGL ES 状态机的 GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER “插槽”,并且对应的绘制指令又是 glDrawElements (都有 Element),因此 IBO 也被称为 EBO。
index_buffer_object.h
#pragma once #include "core_lib.h" namespace glcore { /** * 顶点索引缓冲对象 (简称IBO) * @author little fat sheep */ class IndexBufferObject { private: GLuint m_iboHandle; // IBO句柄 GLuint m_usage; // GL_STATIC_DRAW 或 GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW GLenum m_type = GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT; // 索引数据类型 (GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT 或 GL_UNSIGNED_INT) const void* m_indices; // 顶点索引数据(short*或int*类型) int m_indexNum = 0; // 索引个数 int m_bytes = 0; // 顶点索引字节数 bool m_isDirty = false; // 是否有脏数据 (缓存的数据需要更新) bool m_isBound = false; // 是否已绑定到IBO public: IndexBufferObject(bool isStatic); IndexBufferObject(bool isStatic, GLenum type); ~IndexBufferObject(); void setIndices (void* indices, int bytes); void setIndices (void* indices, int bytes, GLenum type); void bind(); void unbind(); int getNumIndices() { return m_indexNum; } GLenum getType() { return m_type; } private: void applyBufferData(); // 缓存数据 int getTypeSize(); // 获取type对应的字节数 }; } // namespace glcore index_buffer_object.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "glcore/gl_inspector.h" #include "glcore/index_buffer_object.h" #define TAG "IndexBufferObject" namespace glcore { IndexBufferObject::IndexBufferObject(bool isStatic): IndexBufferObject(isStatic, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT) { } IndexBufferObject::IndexBufferObject(bool isStatic, GLenum type) { m_usage = isStatic ? GL_STATIC_DRAW : GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW; m_type = type; GL_CALL(glGenBuffers(1, &m_iboHandle)); printf("%s: init: %dn", TAG, m_iboHandle); } IndexBufferObject::~IndexBufferObject() { printf("%s: destroyn", TAG); GL_CALL(glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0)); GL_CALL(glDeleteBuffers(1, &m_iboHandle)); m_iboHandle = 0; delete[] m_indices; } void IndexBufferObject::setIndices(void* indices, int bytes) { setIndices(indices, bytes, m_type); } void IndexBufferObject::setIndices(void* indices, int bytes, GLenum type) { m_indices = indices; m_type = type; m_indexNum = bytes > 0 ? bytes / getTypeSize() : 0; m_bytes = bytes; m_isDirty = true; if (m_isBound) { applyBufferData(); } } void IndexBufferObject::bind() { GL_CALL(glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, m_iboHandle)); if (m_isDirty) { applyBufferData(); } m_isBound = true; } void IndexBufferObject::unbind() { GL_CALL(glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0)); m_isBound = false; } void IndexBufferObject::applyBufferData() { GL_CALL(glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, m_bytes, m_indices, m_usage)); //GLInspector::checkGLError("ibo: glBufferData"); m_isDirty = false; } int IndexBufferObject::getTypeSize() { switch (m_type) { case GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT: return 2; case GL_UNSIGNED_INT: return 4; } return 2; } } // namespace glcore 2.11 Mesh
Mesh 是网格类,用于管理顶点数据、索引、描述(或格式)等信息,由于 VBO 管理了顶点数据、IBO 管理了顶点索引、VAO 管理了顶点描述(或格式),因此 Mesh 只需管理 VBO、IBO、VAO。另外 IBO 和 VAO 是可选的,Mesh 中需要根据用户的行为调整渲染指令。
为方便用户快速创建平面网格,笔者提供了 MeshUtils 类,用户也可以根据该类提供的模板创建自己的网格。
mesh.h
#pragma once #include <initializer_list> #include "core_lib.h" #include "index_buffer_object.h" #include "shader_program.h" #include "vertex_buffer_object.h" #include "vertex_attribute.h" #include "vertex_attributes.h" using namespace std; namespace glcore { /** * 网格 * @author little fat sheep */ class Mesh { private: VertexBufferObject* m_vbo; // 顶点属性缓冲对象 IndexBufferObject* m_ibo; // 顶点索引缓冲对象 public: Mesh(bool isStatic, initializer_list<VertexAttribute*> attributes); Mesh(bool isStatic, VertexAttributes* attributes); Mesh(bool useVao, bool isStatic, initializer_list<VertexAttribute*> attributes); Mesh(bool useVao, bool isStatic, VertexAttributes* attributes); ~Mesh(); void setVertices(float* vertices, int bytes); // 设置顶点属性 void setIndices(void* indices, int bytes); // 设置顶点索引 void setIndices(void* indices, int bytes, GLenum type); // 设置顶点索引 void render(ShaderProgram* shader, GLenum primitiveType); // 渲染 }; } // namespace glcore mesh.cpp
#include "glcore/gl_inspector.h" #include "glcore/mesh.h" #include "glcore/vertex_buffer_object_with_vao.h" namespace glcore { Mesh::Mesh(bool isStatic, initializer_list<VertexAttribute*> attributes): Mesh(true, isStatic, new VertexAttributes(attributes)) { } Mesh::Mesh(bool isStatic, VertexAttributes* attributes): Mesh(true, isStatic, attributes) { } Mesh::Mesh(bool useVao, bool isStatic, initializer_list<VertexAttribute*> attributes): Mesh(useVao, isStatic, new VertexAttributes(attributes)) { } Mesh::Mesh(bool useVao, bool isStatic, VertexAttributes* attributes) { m_vbo = useVao ? new VertexBufferObjectWithVAO(isStatic, attributes) : new VertexBufferObject(isStatic, attributes); m_ibo = new IndexBufferObject(isStatic); } Mesh::~Mesh() { delete m_vbo; delete m_ibo; } void Mesh::setVertices(float* vertices, int bytes) { m_vbo->setVertices(vertices, bytes); } void Mesh::setIndices(void* indices, int bytes) { m_ibo->setIndices(indices, bytes); } void Mesh::setIndices(void* indices, int bytes, GLenum type) { m_ibo->setIndices(indices, bytes, type); } void Mesh::render(ShaderProgram* shader, GLenum primitiveType) { m_vbo->bind(shader); if (m_ibo->getNumIndices() > 0) { m_ibo->bind(); GL_CALL(glDrawElements(primitiveType, m_ibo->getNumIndices(), m_ibo->getType(), nullptr)); m_ibo->unbind(); } else { GL_CALL(glDrawArrays(primitiveType, 0, m_vbo->getNumVertices())); } m_vbo->unbind(shader); } } // namespace glcore mesh_utils.h
#pragma once #include "mesh.h" namespace glcore { /** * 网格工具类 * @author little fat sheep */ class MeshUtils { public: static Mesh* createRect(bool reverse); private: static float* getRectVertices(bool reverse); }; } // namespace glcore mesh_utils.cpp
#include "glcore/mesh_utils.h" namespace glcore { Mesh* MeshUtils::createRect(bool reverse) { Mesh* mesh = new Mesh(true, { VertexAttribute::Position(), VertexAttribute::TexCoords(0) }); float* vertices = getRectVertices(reverse); mesh->setVertices(vertices, 4 * 5 * sizeof(float)); void* indices = new short[6] { 0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 0 }; mesh->setIndices(indices, 6 * sizeof(short)); return mesh; } float* MeshUtils::getRectVertices(bool reverse) { if (reverse) { return new float[20] { // 中间渲染(FBO)使用 -1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // 左下 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // 右下 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // 右上 -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f // 左上 }; } return new float[20] { // 终端渲染使用 -1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, // 左下 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // 右下 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // 右上 -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f // 左上 }; } } // namespace glcore 2.12 GLTexture
封装 GLTexture 类是了方便用户进行纹理贴图。为了方便管理多渲染目标图层,定义了 TextureAction 接口,并提供 bind 函数,GLTexture、FBO 都继承了 TextureAction,用户自定义的渲染器或特效类也可以继承 TextureAction,将它们统一视为纹理活动(可绑定),这在特效叠加(或后处理)中非常有用,易于扩展。
texture_action.h
#pragma once #include "core_lib.h" #include "shader_program.h" namespace glcore { /** * 纹理活动 (纹理绑定、FBO绑定) * @author little fat sheep */ class TextureAction { public: virtual ~TextureAction() = default; virtual void setTexParameter(GLint filter, GLint wrap) {} virtual void setBindParameter(char* alias, GLenum unit) {} virtual void bind(ShaderProgram* shader) = 0; }; } // namespace glcore gl_texture.h
#pragma once #include "core_lib.h" #include "shader_program.h" #include "texture_action.h" namespace glcore { /** * 纹理贴图 * @author little fat sheep */ class GLTexture: public TextureAction { private: GLuint m_textureHandle = 0; // 纹理句柄 int m_width = 0; // 纹理宽度 int m_height = 0; // 纹理高度 GLint m_filter = GL_LINEAR; // 滤波方式 GLint m_wrap = GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE; // 环绕方式 const char* m_alias = ShaderProgram::UNIFORM_TEXTURE; // 纹理别名(着色器中变量名) GLenum m_unit = 0; // 纹理单元 (可能有多个纹理) bool m_isDirty = false; // 是否有脏数据 (纹理参数需要更新) public: GLTexture(int width, int height); GLTexture(void *buffer, int width, int height); ~GLTexture() override; void setTexture(const void *buffer); void setTexParameter(GLint filter, GLint wrap) override; void setBindParameter(char* alias, GLenum unit) override; void bind(ShaderProgram* shader) override; int getWidth() { return m_width; } int getHeight() { return m_height; } private: void applyTexParameter(); }; } // namespace glcore gl_texture.cpp
#include "glcore/gl_inspector.h" #include "glcore/gl_texture.h" namespace glcore { GLTexture::GLTexture(int width, int height): m_width(width), m_height(height) { } GLTexture::GLTexture(void *buffer, int width, int height): GLTexture(width, height) { setTexture(buffer); } GLTexture::~GLTexture() { GL_CALL(glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0)); if (m_textureHandle != 0) { GL_CALL(glDeleteTextures(1, &m_textureHandle)); m_textureHandle = 0; } } /** * buffer 可以通过以下两种方式得到 * void* buffer = stbi_load(filePath, &width, &height, &channels, STBI_rgb_alpha) */ void GLTexture::setTexture(const void *buffer) { GL_CALL(glGenTextures(1, &m_textureHandle)); GL_CALL(glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_textureHandle)); applyTexParameter(); GL_CALL(glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA, m_width, m_height, 0, GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, buffer)); GL_CALL(glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D)); GL_CALL(glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0)); //GLInspector::checkGLError("setTexture"); } void GLTexture::setTexParameter(GLint filter, GLint wrap) { m_filter = filter; m_wrap = wrap; m_isDirty = true; } void GLTexture::setBindParameter(char *alias, GLenum unit) { m_alias = alias; m_unit = unit; } void GLTexture::bind(ShaderProgram *shader) { shader->setUniformi(m_alias, m_unit); GL_CALL(glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0 + m_unit)); GL_CALL(glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_textureHandle)); if (m_isDirty) { applyTexParameter(); } } void GLTexture::applyTexParameter() { GL_CALL(glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, m_filter)); GL_CALL(glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, m_filter)); GL_CALL(glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, m_wrap)); GL_CALL(glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, m_wrap)); m_isDirty = false; } } // namespace glcore 2.13 FBO
FBO 是 Frame Buffer Object 的简称,即帧缓冲对象,主要用于离屏渲染、特效叠加,
frame_buffer_object.h
#pragma once #include "core_lib.h" #include "shader_program.h" #include "texture_action.h" #include "format.h" namespace glcore { /** * 帧缓冲对象 (简称FBO, 用于离屏渲染) * @author little fat sheep */ class FrameBufferObject: public TextureAction { private: Format* m_format; // 颜色格式 int m_width; // 缓冲区宽度 int m_height; // 缓冲区高度 bool m_hasDepth; // 是否有深度缓冲区 bool m_hasStencil; // 是否有模板缓冲区 GLuint m_frameBufferHandle; // 帧缓冲区句柄 GLuint m_depthBufferHandle; // 深度缓冲区句柄 GLuint m_stencilBufferHandle; // 模板缓冲区句柄 GLuint m_colorTextureHandle; // 颜色缓冲区句柄 GLint m_preFramebufferHandle; // 前一个帧缓冲区句柄 int m_preFramebufferViewPort[4]; // 前一个帧缓冲区视口 GLint m_filter = GL_LINEAR; // 滤波方式 GLint m_wrap = GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE; // 环绕方式 const char* m_alias = ShaderProgram::UNIFORM_TEXTURE; // 纹理别名(着色器中变量名) GLenum m_unit = 0; // 纹理单元 (可能有多个纹理) bool m_isDirty = true; // 是否有脏数据 (纹理参数需要更新) public: FrameBufferObject(Format* format, int width, int height, bool hasDepth, bool hasStencil); ~FrameBufferObject() override; void setTexParameter(GLint filter, GLint wrap) override; void setBindParameter(char* alias, GLenum unit) override; void begin(); // 开始将内容渲染到fbo void end(); // 结束将内容渲染到fbo void bind(ShaderProgram* shader) override; private: void applyTexParameter(); }; } // namespace glcore frame_buffer_object.cpp
#include "glcore/frame_buffer_object.h" #include "glcore/gl_inspector.h" namespace glcore { FrameBufferObject::FrameBufferObject(Format* format, int width, int height, bool hasDepth, bool hasStencil) { m_format = format; m_width = width; m_height = height; m_hasDepth = hasDepth; m_hasStencil = hasStencil; GL_CALL(glGenFramebuffers(1, &m_frameBufferHandle)); begin(); if (m_hasDepth) { GL_CALL(glGenRenderbuffers(1, &m_depthBufferHandle)); GL_CALL(glBindRenderbuffer(GL_RENDERBUFFER, m_depthBufferHandle)); GL_CALL(glRenderbufferStorage(GL_RENDERBUFFER, GL_DEPTH_COMPONENT16, width, height)); GL_CALL(glFramebufferRenderbuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_DEPTH_ATTACHMENT, GL_RENDERBUFFER, m_depthBufferHandle)); GL_CALL(glBindRenderbuffer(GL_RENDERBUFFER, 0)); } if (m_hasStencil) { GL_CALL(glGenRenderbuffers(1, &m_stencilBufferHandle)); GL_CALL(glBindRenderbuffer(GL_RENDERBUFFER, m_stencilBufferHandle)); GL_CALL(glRenderbufferStorage(GL_RENDERBUFFER, GL_STENCIL_INDEX8, width, height)); GL_CALL(glFramebufferRenderbuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_STENCIL_ATTACHMENT, GL_RENDERBUFFER, m_stencilBufferHandle)); GL_CALL(glBindRenderbuffer(GL_RENDERBUFFER, 0)); } GL_CALL(glGenTextures(1, &m_colorTextureHandle)); GL_CALL(glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_colorTextureHandle)); GL_CALL(glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, m_format->getFormat(), m_width, m_height, 0, m_format->getFormat(), m_format->getType(), nullptr)); applyTexParameter(); GL_CALL(glFramebufferTexture2D(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, GL_COLOR_ATTACHMENT0, GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_colorTextureHandle, 0)); end(); } FrameBufferObject::~FrameBufferObject() { GL_CALL(glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0)); GL_CALL(glDeleteTextures(1, &m_colorTextureHandle)); if (m_hasDepth) { GL_CALL(glDeleteRenderbuffers(1, &m_depthBufferHandle)); } if (m_hasStencil) { GL_CALL(glDeleteRenderbuffers(1, &m_stencilBufferHandle)); } GL_CALL(glDeleteFramebuffers(1, &m_frameBufferHandle)); } void FrameBufferObject::setTexParameter(GLint filter, GLint wrap) { m_filter = filter; m_wrap = wrap; m_isDirty = true; } void FrameBufferObject::setBindParameter(char* alias, GLenum unit) { m_alias = alias; m_unit = unit; } void FrameBufferObject::begin() { GL_CALL(glGetIntegerv(GL_FRAMEBUFFER_BINDING, &m_preFramebufferHandle)); GL_CALL(glGetIntegerv(GL_VIEWPORT, m_preFramebufferViewPort)); GL_CALL(glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, m_frameBufferHandle)); GL_CALL(glViewport(0, 0, m_width, m_height)); } void FrameBufferObject::end() { GL_CALL(glBindFramebuffer(GL_FRAMEBUFFER, m_preFramebufferHandle)); GL_CALL(glViewport(m_preFramebufferViewPort[0], m_preFramebufferViewPort[1], m_preFramebufferViewPort[2], m_preFramebufferViewPort[3])); } void FrameBufferObject::bind(ShaderProgram* shader) { shader->setUniformi(m_alias, m_unit); GL_CALL(glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0 + m_unit)); GL_CALL(glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, m_colorTextureHandle)); if (m_isDirty) { applyTexParameter(); } } void FrameBufferObject::applyTexParameter() { GL_CALL(glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, m_filter)); GL_CALL(glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, m_filter)); GL_CALL(glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, m_wrap)); GL_CALL(glTexParameterf(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, m_wrap)); m_isDirty = false; } } // namespace glcore format.h
#pragma once #include "core_lib.h" namespace glcore { /** * 纹理格式 * @author little fat sheep */ class Format { private: GLint format; GLenum type; public: Format(GLint format, GLenum type); GLint getFormat() { return format; } GLenum getType() { return type; } static Format* Alpha(); static Format* LuminanceAlpha(); static Format* RGB565(); static Format* RGBA4444(); static Format* RGB888(); static Format* RGBA8888(); }; } // namespace glcore format.cpp
#include "glcore/format.h" namespace glcore { Format::Format(GLint format, GLenum type): format(format), type(type) { } Format *Format::Alpha() { return new Format(GL_ALPHA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE); } Format *Format::RGB565() { return new Format(GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT_5_6_5); } Format *Format::RGBA4444() { return new Format(GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT_4_4_4_4); } Format *Format::RGB888() { return new Format(GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE); } Format *Format::RGBA8888() { return new Format(GL_RGBA, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE); } } // namespace glcore 3 工具相关
本节主要介绍 glcore 框架在初始化过程中所依附的工具类,如字符串加载工具、图片加载工具等,它们与平台相关(如 Android 平台字符串和图片加载依赖 JNI),不便于进行跨平台迁移,因此不能将它们归入 glcore 框架中。
3.1 StringUtils
StringUtils 用于加载顶点和片元着色器资源为字符串。
string_utils.h
#pragma once /** * String工具类 * @author little fat sheep */ class StringUtils { public: /** * 根据资源路径读取字符串 * @param filePath 资源文件路径, 如: "assets/shaders/vertex_shader.glsl" */ static const char* loadStringFromFile(const char* filePath); }; string_utils.cpp
#include <fstream> #include <sstream> #include <string> #include "utils/string_utils.h" using namespace std; const char* StringUtils::loadStringFromFile(const char* filePath) { ifstream file(filePath); if (!file.is_open()) { printf("failed to open file: %sn", filePath); return nullptr; } stringstream buffer; buffer << file.rdbuf(); file.close(); string content = buffer.str(); // 复制字符串, 避免content被回收导致悬垂指针问题 char * res = strdup(content.c_str()); return res; } 3.2 BitmapUtils
BitmapUtils 用于加载图片资源为位图。为了方便加载各种格式的资源,使用了 stb_image 工具,详见 → https://github.com/nothings/stb。
bitmap_utils.h
#pragma once struct BitmapData { void* buffer; int width; int height; }; /** * Bitmap工具类 * @author little fat sheep */ class BitmapUtils { public: /** * 根据资源文件路径读取bitmap * @param filePath 资源路径, 如: "assets/textures/xxx.jpg" */ static BitmapData* loadBitmapDataFromFile(const char* filePath); }; bitmap_utils.cpp
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION #include "stb/stb_image.h" #include "utils/bitmap_utils.h" BitmapData* BitmapUtils::loadBitmapDataFromFile(const char* filePath) { int width, height, channels; unsigned char* data = stbi_load(filePath, &width, &height, &channels, STBI_rgb_alpha); BitmapData* bitmapData = new BitmapData(); bitmapData->buffer = data; bitmapData->width = width; bitmapData->height = height; return bitmapData; } 4 应用
本节将基于 glcore 框架写一个色散特效叠加果冻特效的 Demo,体验一下 glcore 的便捷之处。
4.1 MyRenderer
my_renderer.h
#pragma once #include "glcore/core.h" #include "dispersion_effect.h" #include "jelly_effect.h" using namespace glcore; /** * 自定义渲染器 * @author little fat sheep */ class MyRenderer : public EGLSurfaceView::Renderer { private: DispersionEffect* m_dispersionEffect; JellyEffect* m_jellyEffect; long m_startTime = 0; float m_runTime = 0.0f; public: MyRenderer(); ~MyRenderer() override; void onSurfaceCreated() override; void onSurfaceChanged(int width, int height) override; void onDrawFrame() override; private: long getTimestamp(); }; my_renderer.cpp
#include <chrono> #include <iostream> #include "glcore/core.h" #include "render/my_renderer.h" #define TAG "MyRenderer" using namespace glcore; using namespace std::chrono; MyRenderer::MyRenderer() { printf("%s: initn", TAG); m_dispersionEffect = new DispersionEffect(); m_jellyEffect = new JellyEffect(); m_jellyEffect->setTexAction(m_dispersionEffect); } MyRenderer::~MyRenderer() { printf("%s: destroyn", TAG); delete m_dispersionEffect; delete m_jellyEffect; } void MyRenderer::onSurfaceCreated() { printf("%s: onSurfaceCreatedn", TAG); m_dispersionEffect->onCreate(); m_jellyEffect->onCreate(); GL_CALL(glClearColor(0.1f, 0.2f, 0.3f, 0.4f)); m_startTime = getTimestamp(); } void MyRenderer::onSurfaceChanged(int width, int height) { printf("%s: onSurfaceChanged, width: %d, height: %dn", TAG, width, height); glViewport(0, 0, width, height); m_dispersionEffect->onResize(width, height); m_jellyEffect->onResize(width, height); } void MyRenderer::onDrawFrame() { m_runTime = (getTimestamp() - m_startTime) / 1000.0f; GL_CALL(glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT)); m_dispersionEffect->onDraw(m_runTime); m_jellyEffect->onDraw(m_runTime); } long MyRenderer::getTimestamp() { auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now(); // 获取当前时间 auto duration = now.time_since_epoch(); // 转换为自纪元以来的时间 return duration_cast<milliseconds>(duration).count(); } 4.2 DispersionEffect
DispersionEffect 是色散特效。
dispersion_effect.h
#pragma once #include "glcore/core.h" using namespace glcore; /** * 色散特效 * @author little fat sheep */ class DispersionEffect: public TextureAction { private: ShaderProgram* m_program; Mesh* m_mesh; GLTexture* m_glTexture; FrameBufferObject* m_fbo; public: DispersionEffect(); ~DispersionEffect() override; void onCreate(); void onResize(int width, int height); void onDraw(float runtime); void bind(ShaderProgram* shader) override; private: void createProgram(); void createTexture(); }; dispersion_effect.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "glcore/core.h" #include "render/dispersion_effect.h" #include "utils/bitmap_utils.h" #include "utils/string_utils.h" #define TAG "DispersionEffect" using namespace glcore; DispersionEffect::DispersionEffect() { printf("%s: initn", TAG); } DispersionEffect::~DispersionEffect() { printf("%s: destroyn", TAG); delete m_program; delete m_mesh; delete m_glTexture; delete m_fbo; } void DispersionEffect::onCreate() { printf("%s: onCreaten", TAG); createProgram(); createTexture(); m_mesh = MeshUtils::createRect(true); m_fbo = new FrameBufferObject(Format::RGBA8888(), app->width, app->height, false, false); } void DispersionEffect::onResize(int width, int height) { printf("%s: onResize, width: %d, height: %dn", TAG, width, height); } void DispersionEffect::onDraw(float runtime) { m_fbo->begin(); m_program->bind(); m_program->setUniformf("u_time", runtime); m_program->setUniformf("u_aspect", app->aspect); m_glTexture->bind(m_program); m_mesh->render(m_program, GL_TRIANGLES); m_fbo->end(); } void DispersionEffect::bind(ShaderProgram* shader) { m_fbo->bind(shader); } void DispersionEffect::createProgram() { printf("%s: createProgramn", TAG); const char* vertexCode = StringUtils::loadStringFromFile("assets/shaders/dispersion_vert.glsl"); const char* fragmentCode = StringUtils::loadStringFromFile("assets/shaders/dispersion_frag.glsl"); m_program = new ShaderProgram(vertexCode, fragmentCode); } void DispersionEffect::createTexture() { printf("%s: createTexturen", TAG); BitmapData* data = BitmapUtils::loadBitmapDataFromFile("assets/textures/girl.jpg"); m_glTexture = new GLTexture(data->buffer, data->width, data->height); } dispersion_vert.glsl
attribute vec4 a_position; attribute vec2 a_texCoord0; varying vec2 v_texCoord; void main() { gl_Position = a_position; v_texCoord = a_texCoord0; } dispersion_frag.glsl
precision highp float; uniform float u_aspect; uniform float u_time; uniform sampler2D u_texture; varying vec2 v_texCoord; vec2 getOffset() { // 偏移函数 float time = u_time * 1.5; vec2 dire = vec2(sin(time), cos(time)); float strength = sin(u_time * 2.0) * 0.004; return dire * strength * vec2(1.0, 1.0 / u_aspect); } void main() { vec2 offset = getOffset(); vec4 color = texture2D(u_texture, v_texCoord); color.r = texture2D(u_texture, v_texCoord + offset).r; color.b = texture2D(u_texture, v_texCoord - offset).b; gl_FragColor = color; } 4.3 JellyEffect
JellyEffect 是果冻特效。
jelly_effect.h
#pragma once #include "glcore/core.h" using namespace glcore; /** * 果冻特效 * @author little fat sheep */ class JellyEffect { private: ShaderProgram* m_program; Mesh* m_mesh; TextureAction* m_texAction; public: JellyEffect(); ~JellyEffect(); void setTexAction(TextureAction* texAction); void onCreate(); void onResize(int width, int height); void onDraw(float runtime); private: void createProgram(); }; jelly_effect.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "glcore/core.h" #include "render/jelly_effect.h" #include "utils/string_utils.h" #define TAG "JellyEffect" using namespace glcore; JellyEffect::JellyEffect() { printf("%s: initn", TAG); } JellyEffect::~JellyEffect() { printf("%s: destroyn", TAG); delete m_program; delete m_mesh; } void JellyEffect::setTexAction(TextureAction* texAction) { m_texAction = texAction; } void JellyEffect::onCreate() { printf("%s: onCreaten", TAG); createProgram(); m_mesh = MeshUtils::createRect(false); } void JellyEffect::onResize(int width, int height) { printf("%s: onResize, width: %d, height: %dn", TAG, width, height); } void JellyEffect::onDraw(float runtime) { m_program->bind(); m_program->setUniformf("u_time", runtime); m_program->setUniformf("u_aspect", app->aspect); m_texAction->bind(m_program); m_mesh->render(m_program, GL_TRIANGLE_FAN); } void JellyEffect::createProgram() { printf("%s: createProgramn", TAG); const char* vertexCode = StringUtils::loadStringFromFile("assets/shaders/jelly_vert.glsl"); const char* fragmentCode = StringUtils::loadStringFromFile("assets/shaders/jelly_frag.glsl"); m_program = new ShaderProgram(vertexCode, fragmentCode); } jelly_vert.glsl
attribute vec4 a_position; attribute vec2 a_texCoord0; varying vec2 v_texCoord; void main() { gl_Position = a_position; v_texCoord = a_texCoord0; } jelly_frag.glsl
precision highp float; uniform float u_aspect; uniform float u_time; uniform sampler2D u_texture; varying vec2 v_texCoord; vec2 fun(vec2 center, vec2 uv) { // 畸变函数 vec2 dire = normalize(uv - center); float dist = distance(uv, center); vec2 uv1 = uv + sin(dist * 2.2 + u_time * 3.5) * 0.025; return uv1; } void main() { vec2 uv = vec2(v_texCoord.x, v_texCoord.y / u_aspect); vec2 center = vec2(0.5, 0.5 / u_aspect); vec2 uv1 = fun(center, uv); uv1.y *= u_aspect; gl_FragColor = texture2D(u_texture, uv1); } 4.4 运行效果
运行效果如下,可以看到叠加了色散和果冻特效。

声明:本文转自【OpenGL ES】在Windows上手撕一个mini版的渲染框架。





![洛谷 P11345 [KTSC 2023 R2] 基地简化 题解](http://www.itfaba.com/wp-content/themes/kemi/timthumb.php?src=http://www.itfaba.com/wp-content/themes/kemi/img/random/1.jpg&w=218&h=124&zc=1)
